How to Use Photo Stacking for Daytime Long Exposures
Have you ever tried photographing dreamy landscapes in the daytime with smooth clouds? Then you know the challenges of getting the money shot with just one click.
But what if I tell you that you can achieve that perfect shot through photo stacking? Let’s find out more about what it is and what you can do with it when shooting long exposure photography!

What Is The Purpose of Stacking Photos?
The term stacking simply means combining several photos to create a “master image.”
There are several forms of stacking. The first one is called focus stacking. It combines several pictures with different focus points to create one final image that’s sharp from the foreground to the background.
The second type of stacking is for panorama. Instead of laying one image on top of another, it ‘stitches’ photos side by side to create a panoramic picture.
Finally, the third form of stacking is for long exposure photography which we will be learning today. It combines your image files to enhance anything from moving clouds to waves in the sea.
Each of the stacking methods we mentioned in this article involves a two-step process. The first part is taking a series of pictures, ideally in RAW format.
And the second part is combining them in post-production. The ideal editing suite for this purpose is Photoshop, and that’s what we will be using this tutorial.
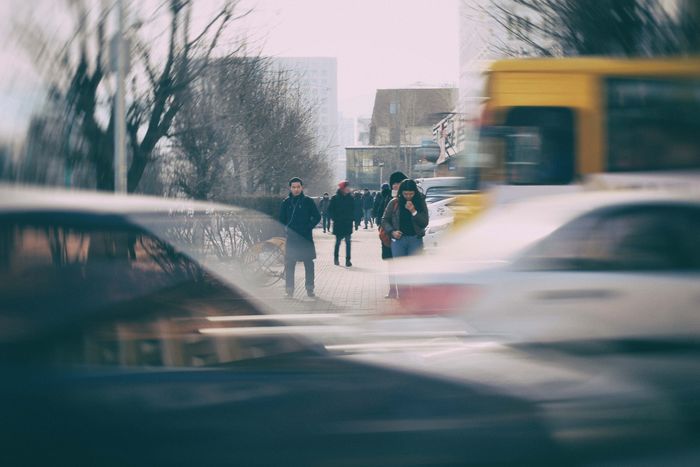

How to Create Perfect Daytime Long-Exposures
When doing long-exposure photography, a lot of problems can easily ruin your shot.
A lot of things can quickly go wrong with an exposure time around 4 minutes. You could encounter all sorts of issues from false light to camera shake. Not to mention vignetting and image noise (hot pixels, thermal noise)!
But by dividing the shot into several shorter exposures, you can overcome most of the issues. You can stack your files together in Adobe Photoshop to achieve that one perfect shot.
Photo stacking is not a technique for every situation. But sometimes stacking your long-exposures is the only way to get a good shot. It’s imperative to know when you need it during shooting.
When to Use Photo Stacking
False Light
At night when the light is limited, you can do 2 or 4 minutes exposures without using neutral density filters.
But during the day, you’ll often have too much light available for long-exposure photography. Using slow shutter speeds in the daytime with a ten-stop ND-filter might still result in an overexposed shot.
Also by narrowing down aperture too much you can encounter problems because of diffraction effect (mostly over f/16).
Photo stacking your daytime long-exposure photos ensures you get correctly exposed shots. You’ll find this especially useful if you don’t own a ten-stop neutral density filter or more.
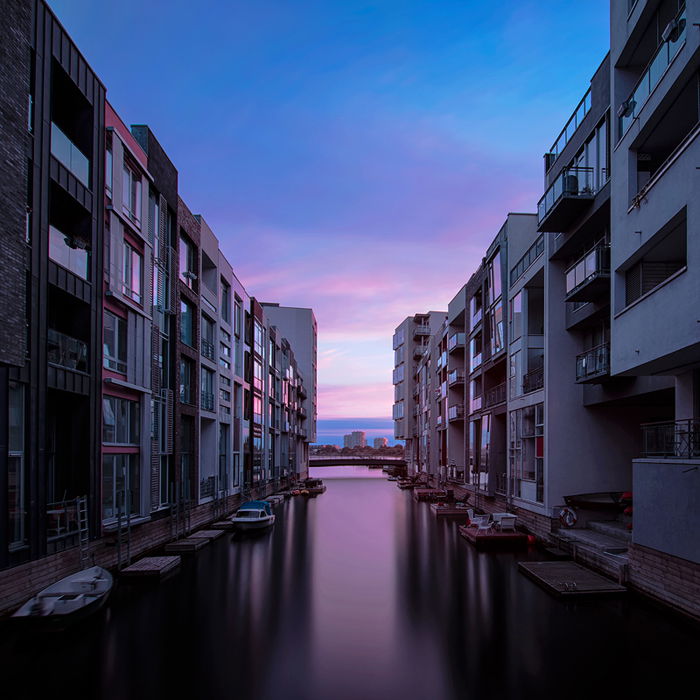

Camera Shake
Besides false light, shaking is the most common reason for failed shots in long-exposure photography.
Since your camera shutter stays open for a few minutes, any movement it records will register as light streaks or motion blur. That’s the same reason why clouds in the sky or the waves in the ocean look wispy.
But small vibrations can also cause motion blur in your camera. Even a breeze or a gentle nudge could easily ruin your shots.
So remember to take the camera strap off your camera while shooting long-exposure. It acts as a sail in the wind and causes shaking to the tripod and camera.
You should also make sure the ground is sturdy enough to support your tripod. Use a remote trigger or self-timer for hands-free operation. Remember that even touching the shutter button could quickly introduce motion blur.
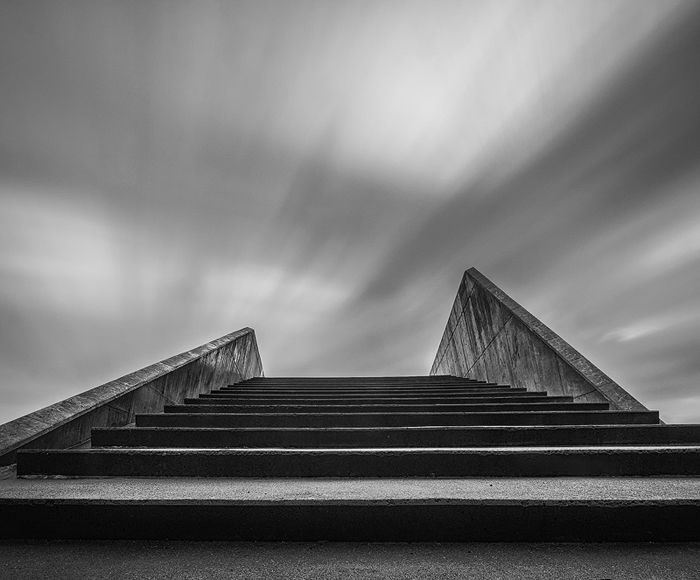

User Error
Of course, we also need to factor in all the unforeseen hiccups that can ruin a great long-exposure shot.
Regardless of whether it’s daytime or night, another common mistake is merely forgetting your remote. Without it, you can only safely go up to 30 seconds, which is the longest exposure time your camera allows.
Bulb mode without a remote requires that you press the shutter all the time. And that’s definitely a no-go if you want to avoid camera shake.
So before you venture out, make sure you have all the equipment you need. In this case, a tripod, ND filters, and your remote trigger will be necessary.
To avoid user error, you should also practice this taking long-exposure images before doing a big project. Becoming familiar with the process allows you to avoid mistakes and even troubleshoot issues.
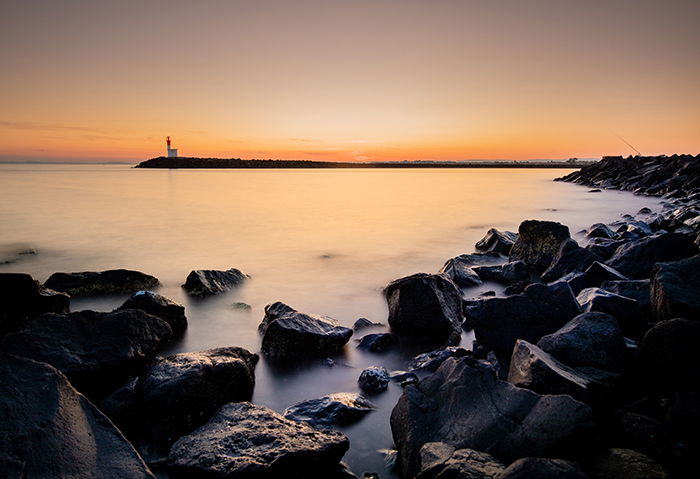

How to Use Photo Stacking for Long-Exposure Photos
We learned a lot about the various issues you may encounter when doing long exposures. Now the question is: How do you take photos for stacking?
In this section, we’ll show you how to do it on the field and how to blend the exposures afterwards in Photoshop.
Setting Up Your Camera
At the location, set up your gear as usual. Make sure your camera settings and ND-filters produce the correct exposure. Your histogram should peak just over the middle to the right when using an exposure time of 30 seconds.
To get the effect of a 4-minute shot, aim for eight good shots, each at 30 seconds (8 x 30 seconds = 4 minutes).
Feel free to take a few test photos to ensure you get the best exposure. Even though you’re stacking pictures, it would help a lot if all the shots you have are usable in the first place.
Get some extra exposures just in case some of them get blurred due to camera shake from a sudden wind gust or bypassing bus. You can leave out a particular shot from your sequence in the photo stacking process.
As you can see, the first part of this process is quite simple. If you’ve done long exposure photography before, this isn’t any different.
The part that you’ll need to learn is how to combine all those pictures in Photoshop. Now, let’s go through the process below.

Post-Processing in Photoshop
Processing your set of daytime long-exposure shots is relatively easy.
From Lightroom, open up your set of shorter long-exposures as layers in Photoshop. You do this in Lightroom’s grid-mode by selecting all the images you want to combine into one exposure.

Right-click and choose Edit In → Edit in Adobe Photoshop.
Don’t select Open as Layers in Photoshop since it’s for focus stacking macro photos. This process is different.
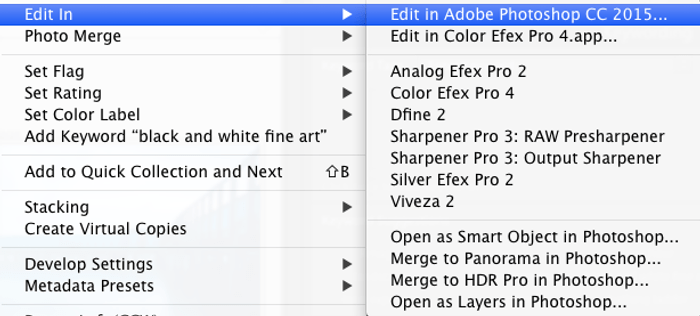
When the images finish loading into Photoshop, go to File → Scripts → Load Files into Stack.
In the appearing dialogue, choose Add Open Files to make the set of images appear under files to use for stacking.
Remember to check Attempt to Automatically Align Source Images and Create Smart Object after Loading Layers.
Click OK to begin the blending process. It usually takes some time for Photoshop to create a single Smart Object from all of the exposures.
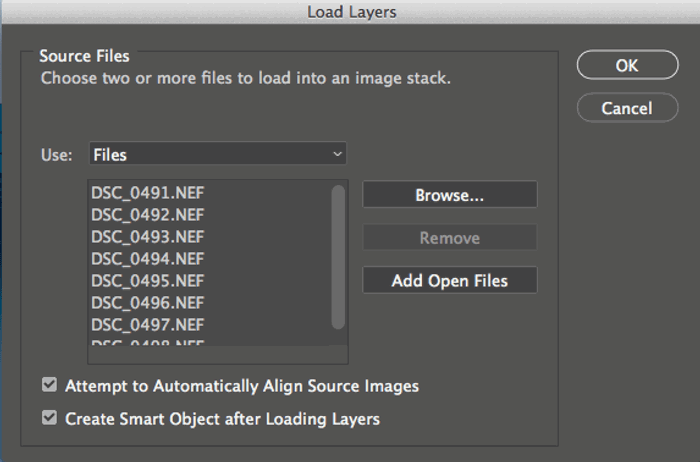
Next, go to the menu Layer → Smart Objects → Stack Mode → Mean. Doing so makes Photoshop automatically blend the images in the stack into a smooth, long-exposure. The goal is to make it look like you took everything as a single long-exposure image.
At this point, you don’t need the layer to be a Smart Object anymore. Keeping it this way would prevent you from using a brush tool, for example. You should convert it by right-clicking on the layer and choose Rasterize Layer.
Next, process the image as you would for a standard daytime long-exposure or any other image. To get the best results, use selective sharpening of the areas in your photo that are not moving.
Long-exposures taken during daytime often have a lot of large white spots with clouds or silky soft water. Applying sharpening to these areas can cause an unwanted grainy look.
The Result
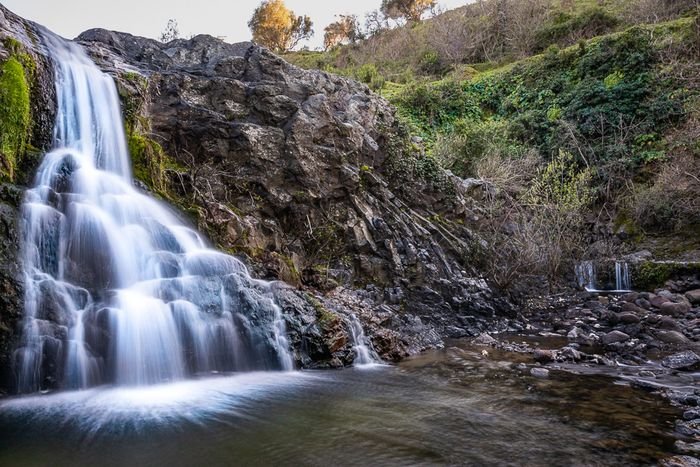
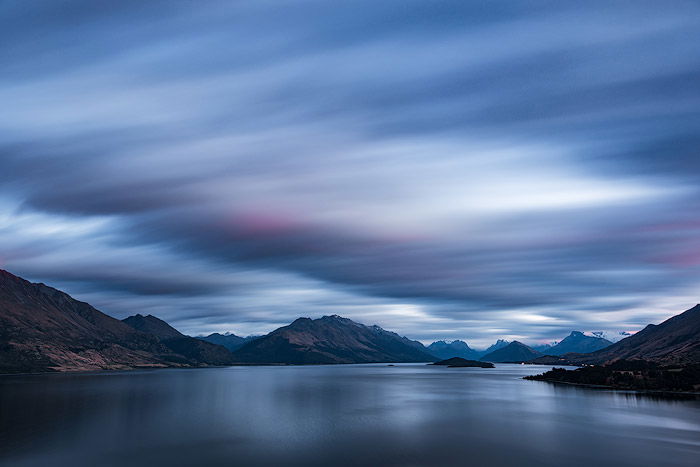
In this particular shot, I had to put my tripod halfway into the water to get the composition I wanted. But it resulted in a blurry 4 min. exposure. The small waves likely transferred a little shaking from the tripod to the camera.
However, by dividing the shot into eight exposures, I got several exposures that were usable for photo stacking.
Daytime long-exposure photography can give you some beautiful and creative results. But it requires patience and practice.
Using photo stacking can save you a lot of time and help you get awesome shots that otherwise might not be possible.
If you’re interested in more great photography ideas, Kindle Unlimited Membership Plans.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------